Diabetic Retinopathy Treatment in Livingston and Morristown, NJ
Diabetic retinopathy is a potentially blinding complication of diabetes mellitus resulting from high sustained levels of blood sugar and sugar byproducts that cause abnormalities within the walls of the tiny blood vessels that nourish the retina. These blood vessels may leak fluid and proteins resulting in swelling of the retina. The fragile capillary bed of the retina may wither and close up resulting in diminished and sometimes absent blood supply. This results in a condition known as ischemia which may also cause an irreversible loss of vision. Progressive abnormal blood vessel and scar tissue growth within the eye may lead to bleeding within the eye and retinal detachment resulting in severe visual dysfunction in poorly controlled diabetic patients.
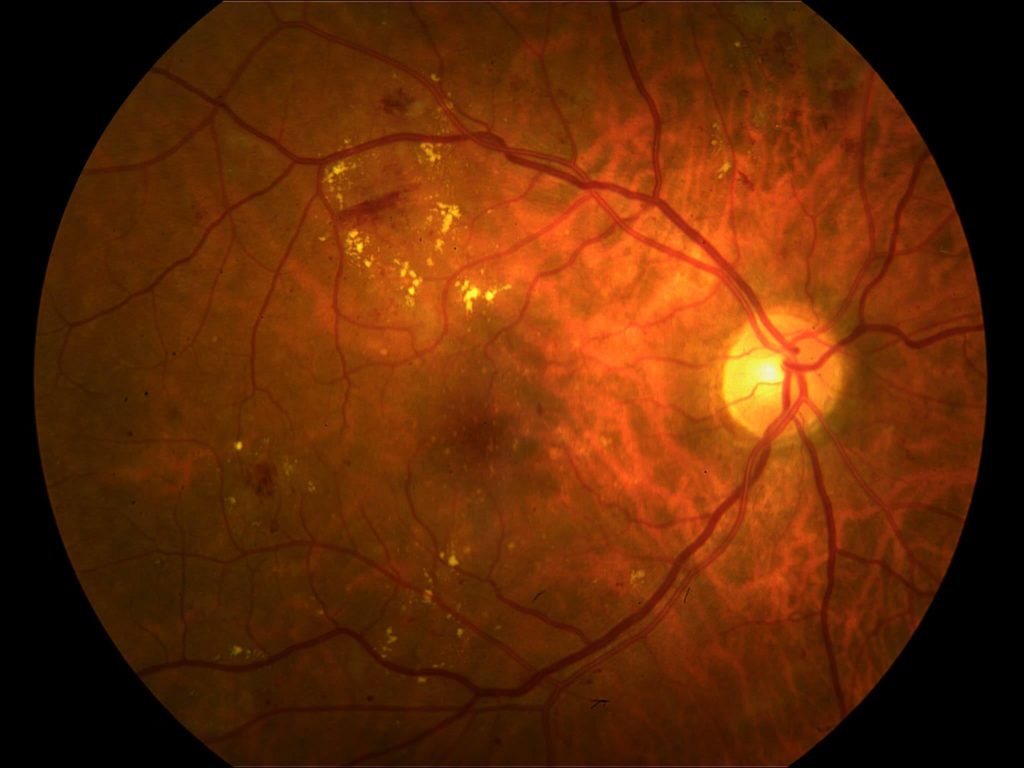
Background diabetic retinopathy of the right eye. Note lipid deposits throughout the eye ground.
What are the stages of Diabetic Retinopathy?
There are two stages of diabetic retinopathy: non-proliferative or background retinopathy, and proliferative retinopathy. The background stage of diabetic retinopathy is an earlier stage of the disease. Vision loss may result from swelling or ischemia of the macula, which is the central portion of the retina responsible for our central reading vision. Proliferative retinopathy is a later, more severe form of the disease. New abnormal blood vessels and scar tissue growth may result in catastrophic loss of vision secondary to bleeding within the eye or retinal detachment.
How do you treat Diabetic Retinopathy?
The clinical nature of the disease will determine the type of treatment recommended by our doctors. Historically, focal laser surgery (photocoagulation) had been indicated in patients who have clinically significant macular edema (CSME) — a specific level of retinal swelling first recognized to be potentially detrimental to vision in a study sponsored by the National Eye Institute. Laser photocoagulation works by helping to “dry up” the swollen retina, thus reducing the chance of progressive vision loss from the disease. The current standard of care, however, has evolved and includes the use of specific medications that are injected directly into the eye. These medications include a group of compounds known as “anti-VEGF” drugs, including Lucentis, Eylea, Avastin, Vabysmo, Eylea HD. Steroids are also used in certain specific cases to help minimize the risk of diabetic vision loss. Retina Vitreous Consultants has been active in investigating the potential use of anti-VEGF injections into the eye in combination with immediate or deferred laser treatment to achieve maximal visual improvement in diabetic eye disease while reducing the treatment burden of frequent intraocular injections.
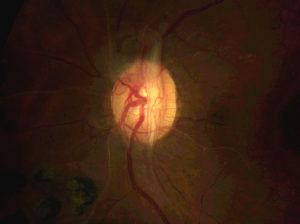
Fibrovascular tissue growing on the surface of the optic nerve as a result of severe proliferative diabetic retinopathy.
Patients suffering from proliferative diabetic retinopathy may benefit from injection of various intraocular medications, pan-retinal photocoagulation (PRP) or a combination of both interventions. Regression of abnormal blood vessel growth and reduction of the potential for intraocular bleeding and scar tissue formation may result in the stabilization of diabetic retinopathy and visual improvement.
Diabetic vision loss secondary to blood or scar tissue within the eye or retinal detachment may be remedied by intraocular surgery. Vitrectomy surgery may be performed to drain blood, remove retinal scar tissue, reattach previously detached retina, and help to rehabilitate vision once impaired by diabetic eye disease.
The very best advice for any diabetic patient to help minimize the risk for vision loss from their disease is prevention, early detection, and prompts intervention. Patients may be completely visually asymptomatic even with moderate to severe forms of diabetic retinopathy. Careful monitoring, as recommended by your physician, will be beneficial to the diabetic patient in maintaining a good level of visual function.
Vitrectomy for Diabetic Eye Disease
Vitrectomy surgery is performed in the operating room setting under sterile conditions. Vitrectomy means “removal of vitreous,” the clear jelly-like substance that fills the inner portion of the eye. In addition to performing vitrectomy for the repair of retinal detachment, vitrectomy surgery may be performed in patients with severe diabetic eye disease who have suffered vision loss secondary to intraocular bleeding and accumulation of scar tissue formation that may cause localized retinal detachment. A smaller subset of individuals, who have unusual retinal anatomic considerations, may experience a poor clinical response to conventional intraocular drug therapy for their diabetic macular swelling. These patients may benefit significantly from vitrectomy surgery. Our doctors will discuss with you and your family at length, and demonstrate to you with your own retinal photographs, scans, and imaging, all of your appropriate surgical options, so that you may make a careful and informed decision in planning your surgical intervention.

Photo of massive bleeding within the left eye secondary to proliferative diabetic retinopathy. Vision is hand motion.

Complete clearance of vitreous hemorrhage following vitrectomy and intraocular laser. Vision improved to 20/20.